Photovoltaic (PV) Solar Systems

Savings with PV Solar
Lower (or no) monthly electric bills, strong incentives, and flexible payment plans make PV solar accessible. Explore your options today.

Start Your Solar Journey
It’s easier than you think to start your journey to solar. Take these simple steps to see how solar can work to meet your needs.

Solar Installation Spotlights
Take a look at real customers who installed a PV solar system on their home or building. Many paired solar with geothermal for ultimate savings.

Free Solar Consultation
Does a PV solar system sound like a solution for you? Answer a few questions, and we’ll get you connected with a local installer for a free design and quote.
How Does a PV Solar System Work?

Photovoltaic (PV) solar modules convert sunlight to electricity through inverters. The electricity is used to power homes, buildings, and cars, and to supplement power grids.
The electricity produced by a solar array is measured in kilowatt-hours or kWh. The amount of kWh produced by the array is dependent on the power rating of the modules and how the system absorbs energy under peak sunlight and optimal operating temperatures. The placement of the array, orientation, shading, and tilt also determines how much energy the system produces, making correct design and installation imperative to ensure the best performance.
Solar modules have no moving parts, typically last 30-plus years, and are low-maintenance.
The Parts of a PV Solar System
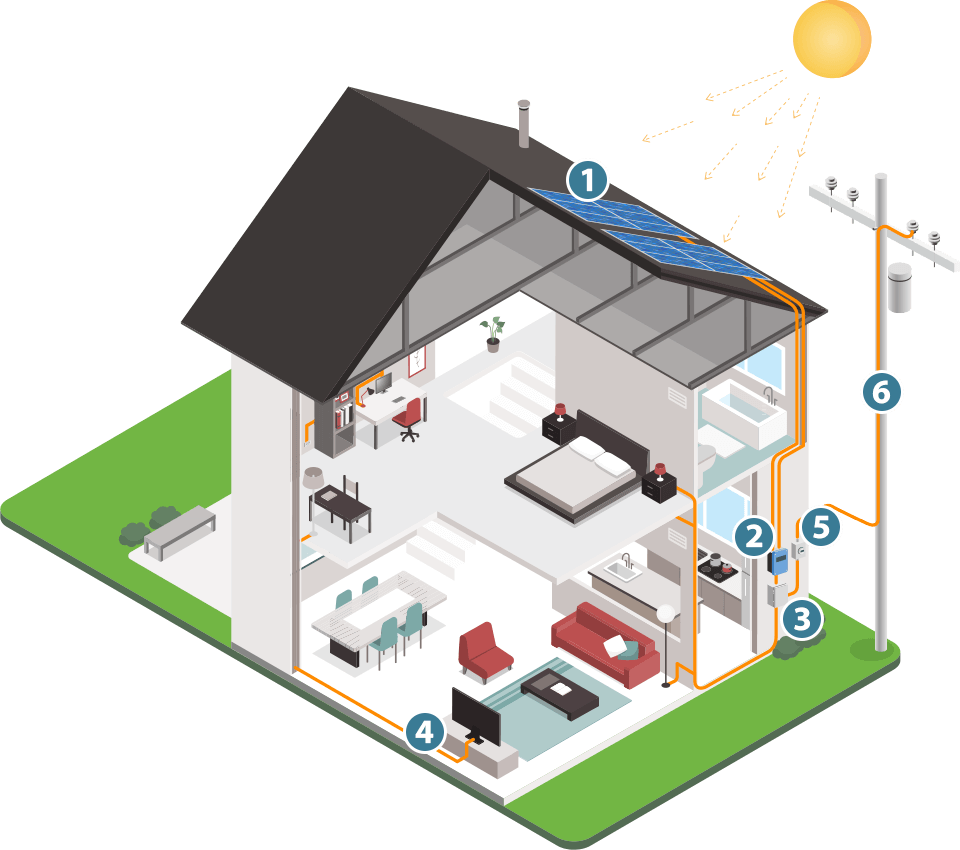
 Solar Modules
Solar Modules
When sunlight hits the surface of a module, the energy is converted to electricity. Photons from the sun’s rays are collected by the solar cells on the modules and pushed through to release electrons. This creates electric energy known as direct current (DC energy).
 Inverter
Inverter
Once the DC electricity is created, it is converted to alternating current (AC) electricity. AC electricity is the standard electricity used to power homes and buildings.
 Breaker Panel
Breaker Panel
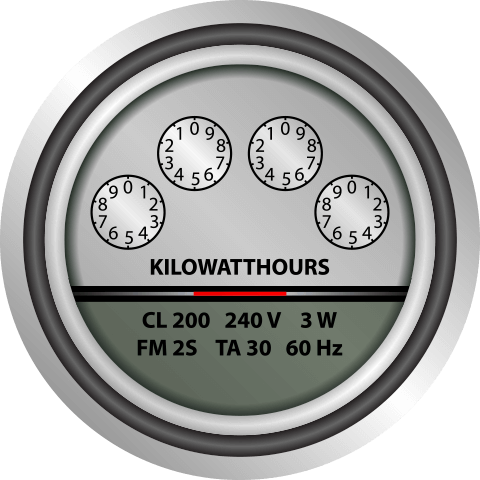
The AC electricity from the inverter is sent to the breaker panel to power your home or building. If there’s excess energy, it will be sent back to the utility grid. The utility meter will monitor and record this credit transfer, making your meter run backward from the excess energy and ultimately providing you with more savings.
 Home Electricity
Home Electricity
Use the sun’s “free” electricity to power everyday items in your home or building. Offset your geothermal heat pump, power your electric car, or charge phone! Energy created by you, for you.
 Net Metering
Net Metering
When your array produces excess energy, it is sent back to the grid (see number 3) for credit with your utility company. Qualifying utility companies provide what’s called a net metering incentive program where they credit your account for excess energy produced. This will result in even lower monthly electric bills and ultimate savings.
 Grid Interconnection
Grid Interconnection
Utility lines act as a transfer for the excess energy produced by a solar array. The excess energy gets sent back to the electric grid through the power lines.
What is Net Metering?
Eliminating or reducing monthly electric and utility bills while providing a sustainable, environmentally-friendly power solution are only some of the reasons adding a solar array to your home or building is beneficial to you and the environment.
A solar PV array’s output will peak mid-day when the sun reaches its highest point. All the energy absorbed will be used for your house or building. If your solar array generates more electricity than the house or building needs, the excess electricity will be credited toward the electricity used during the night when the array has no output. This is called net metering. However, depending on your utility provider, net metering is not an option for all. Net metering allows residential and commercial customers to use the utility provider like a battery. You can generate your own electricity that will feed back into the grid to use at a later time. Customers are only billed on the “net” energy use.




The 4-Step Process to the Best, Energy-Efficient Structure
Step 1: Insulate Right
Invest in an air-tight structure with the latest insulation technology.

Step 2: Install Geothermal
Dramatically lower the structure’s energy demand with a geothermal heat pump. Proper insulation allows for a smaller-sized system, saving on installation costs.
Step 3: Invest in PV Solar
Completing steps one and two allows for fewer solar panels to power most, if not all, of your structure, which saves on install costs.
Step 4: Battery Storage
If you’ve taken steps one through three, storing excess energy through an external battery to use at your disposal instead of sending it back to the grid is an option.
Are you interested in a net-zero home or building? Pairing a geothermal heat pump with a solar array is the best and most cost-effective option. Download the infographic for more details on geothermal + solar.